Depending on the radiation type, the dose, and the length of exposure, radiation could have both good and bad effects on humans. I’ll concentrate specifically on the poor effects of “radiation” on human health here:
Ionizing Radiation Effects:
Ionizing radiation is a kind of radiation that contains sufficient power to cast off tightly sure electrons from atoms, developing ions and probably inflicting damage to biological tissues. This sort of radiation includes sources like X-rays, gamma rays, and different kinds of particles emitted from radioactive materials. Ionizing radiation can have quite a few influences on human beings, depending at the dose, length of exposure, radiation types, and personal physical health. Here are a number of the outcomes:
1. Deterministic Effects:
When the radiation dose is robust enough to directly damage cells and tissues, numerous consequences take vicinity. Below a threshold value, they generally do no longer show up. Examples include cataracts, radiation burns, and acute radiation syndromes (ARS). The dose taken at once affects how severe these side results are.
2. Stochastic Effects:
These facet consequences appear at random and are linked to extended radiation exposure at lower doses. They include genetic mutations and most cancers. For stochastic effects, not like deterministic consequences, there may be no apparent dose threshold; they turn out to be more probable as the dose rises, however even low doses have the capacity to subsequently contribute to those consequences.
3. Cancer:
Cancer is a complicated sickness characterized via the out of control increase of cells. Ionizing radiation poses a vast threat as it may damage the DNA within cells, may causing mutations that cause the onset of cancer. This manner is a essential mechanism underlying radiation-brought about carcinogenesis. However, it is crucial to word that exceptional varieties of cancers show off varying ranges of susceptibility to radiation-prompted development. Some cancers may be extra prone to this hazard, while others may also show off more resistance. Understanding those versions is vital in assessing the capability effect of ionizing radiation on most cancers formation and tailoring effective preventive strategies.

4. Genetic Effects:
Exposure to multiplied levels of ionizing radiation consists of the ability to set off mutations in genetic cells, particularly sperm and eggs. These mutations have the ominous capability of ushering in hereditary genetic results which can reverberate across successive generations. Such disruptions at the genetic level can impart enduring implications for the fitness and nicely-being of descendants, underscoring the important significance of safeguarding against immoderate ionizing radiation exposure to mitigate the chance of putting up with genetic anomalies and their enduring impact on our genetic heritage. Thus, prudent measures and safeguards are imperative to prevent the transmission of detrimental genetic changes that could perpetuate thru time.
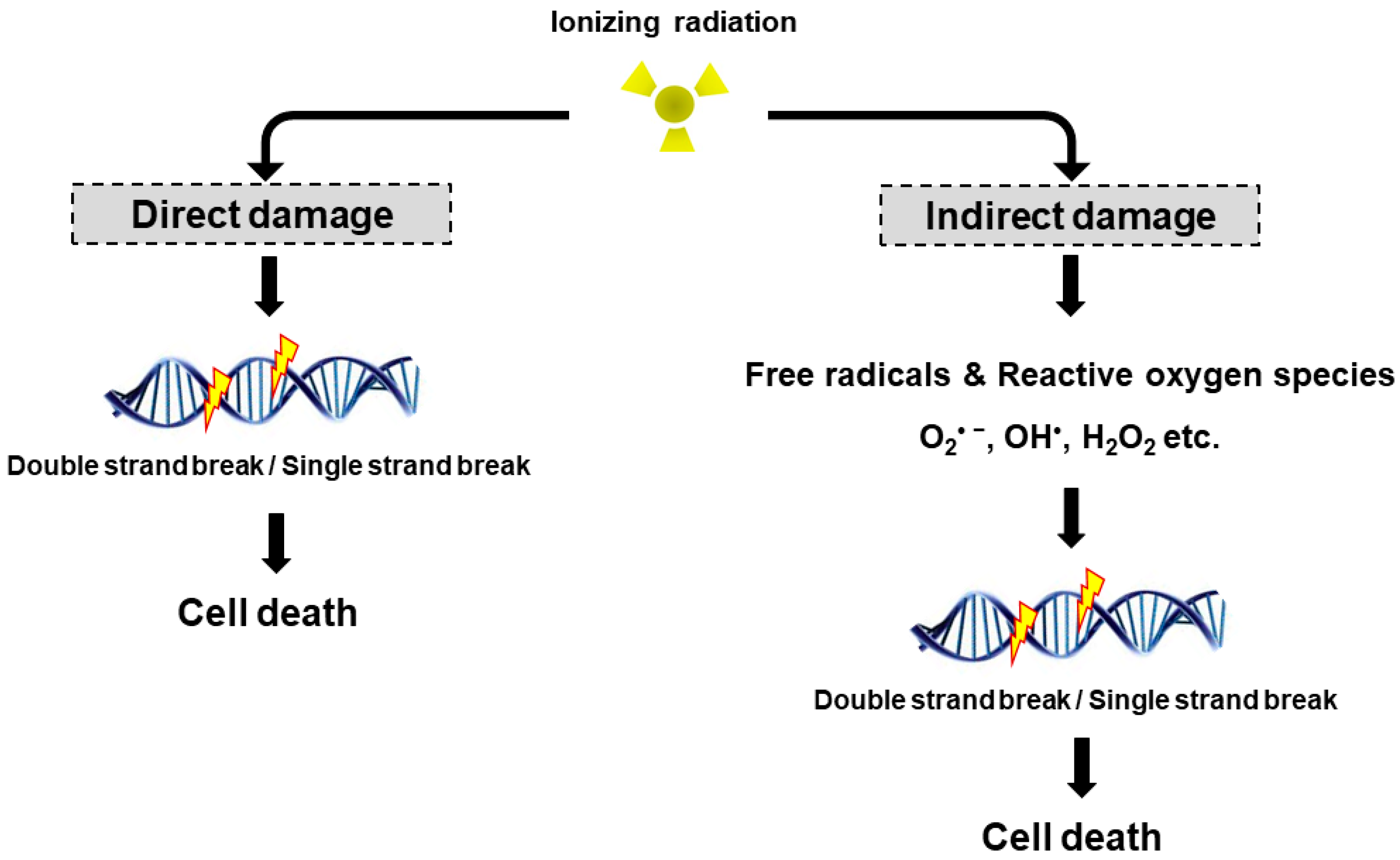
5. Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS):
Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS) is a complicated of symptoms that occur quickly after exposure to ionizing radiation. These symptoms embody nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, skin burns, and damage to the immune and blood-forming structures. The intensity of ARS is contingent upon the radiation dose and the period of exposure to the body. ARS is a severe issue in conditions regarding nuclear damages or radiation therapy long past off-center. Immediate medical interest is crucial for those affected, as set off involvement can mitigate the severity of those distressing symptoms and enhance the probabilities of recovery. Understanding ARS is vital for effective radiation protection management.
6. Long-Term Health Effects:
Long-term health results stemming from continual exposure to low doses of ionizing radiation are a rely of enormous subject. Research has established a clear hyperlink between such exposure and an multiplied hazard of most cancers, with specific emphasis on leukemia, thyroid cancer, and various solid tumors. It is crucial to understand that the degree of threat is generally commensurate with the cumulative dose received through the years. This underscores the importance of stringent radiation protection measures, as even apparently modest and prolonged exposure can probably have excessive health repercussions, making ongoing monitoring and risk mitigation paramount in radiation-extensive environments.
7. Radiation Sickness:
Radiation Sickness, a dangerous condition, emerges following vast exposure to ionizing radiation. Its symptoms embody nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weak spot, and fever, manifesting as the body grapples with the damaging results of radiation. The severity of these effects hinges upon two essential factors: the dose of radiation persisted and the kind of radiation. The more the exposure and the stronger the radiation, the greater profound the resulting sickness. Vigilance and defensive measures are paramount when running in environments with radiation risks to limit the danger of succumbing to this debilitating situation.
8. Tissue and Organ Damage:
Ionizing radiation can damage tissues and organs, mainly causing health issues, impaired organ structure, and reducing the probability of lifespan. The extent to which tissues and organs are sensitive to ionizing radiation ought to be cited. Additionally, some human beings may be specifically more sensitive to radiation, including kids and pregnant women.
Non-Ionizing Radiation Effects:
Non-ionizing radiation would not have sufficient energy to dispose of electrons from an atom considering that its power ranges are less. Radio waves, microwaves, visible light, and specific forms of electromagnetic fields are some examples. Despite the truth that non-ionizing radiation is normally appeared as much less dangerous than ionizing radiation, the subsequent effects had been referred to:
1. Thermal Effects:
Non-ionizing radiation, in particular the microwave and radio frequency spectrum, can induce localized tissue heating. Extended exposure of such radiation may additionally result in harm to the affected tissues. These thermal outcomes arise as power from the radiation is absorbed by means of the frame, causing a rise in temperature inside precise areas. It’s imperative to mitigate extended exposure of non-ionizing radiation to save tissue damage. Safety measures and precautions are crucial in minimizing the risks associated with these thermal effects and ensuring protection of individuals in environments wherein such radiation is prevalent.

2. Electromagnetic Hypersensitivity:
Electromagnetic Hypersensitivity, often referred to as EHS, is a debatable phenomenon. A few people claim that they are disturbed and have signs and symptoms such as complications, fatigue, and difficulty in concentrating when exposed to electromagnetic fields emitted by devices like cellular telephones and Wi-Fi routers. Despite those claims, the medical community remains divided, as rigorous research has not continuously substantiated the lifestyles of EHS. Consequently, the talk surrounding Electromagnetic Hypersensitivity underscores the significance of proof-based tactics to address fitness problems associated with these.
3. Photochemical Effects:
Photochemical effects end result from excessive exposure to particular wavelengths of non-ionizing radiation, extensively UV radiation from the sun. This can trigger photochemical reactions on skin and eyes, culminating in detrimental outcomes like painful sunburn, untimely skin getting older, and an elevated susceptibility to cataracts. It is essential to protect oneself from excessive UV exposure through defensive measures inclusive of sunscreen application, wearing UV-blocking off sunglasses, and proscribing sun exposure at some stage in late hours. These precautions can extensively mitigate the adverse outcomes of extended exposure to UV radiation, protecting both skin and eye health for the long term.
Conclusions:
Now we conclude out topic ‘Effects of Radiation on Human‘. Safety precautions are vital to lessen ionizing radiation risks, especially in commercial settings (nuclear power plant and radiological centers) and clinical settings (together with X-rays and radiation treatment). To prevent humans from being exposed to ionizing radiation without need, regulatory bodies and organization should set guidelines and protection necessities.


excellent blog